Difference Between Critical and Non-Critical Loads
Last updated: 11 May 2025
25 Views

Difference Between Critical and Non-Critical Loads
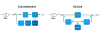
Critical Loads
These are devices or systems essential to the core operations of an organization and must remain operational during a power outage.
Examples include:
- Servers in data centers
- Life support equipment in hospitals
Any failureeven partialcan lead to severe consequences. For this reason, critical loads require uninterrupted power through a UPS or backup generators. In some cases, the objective is not continuous operation but enabling a safe shutdown to prevent data loss or equipment damage.
Non-Critical Loads
These are devices that can stop operating safely during a power outage because they are not essential to business continuity.
Examples include:
- Office printers
- Standard lighting
- Desk fans
Additional Load Categories for General Organizations
Essential Loads
- Not directly tied to business operations but important for safety and functionality
- Includes emergency lighting or critical ventilation
- These may not need continuous power but should run once the backup generator kicks in
Non-Essential Loads
- Acceptable to shut down during outages without impact on safety or operations
- Includes decorative lighting, coffee machines, or peripheral devices
Factors to Consider When Classifying Loads
Determining whether a load is critical or non-critical depends on:
- Financial impact potential revenue loss or customer service disruption
- Operational importance affects core functions or workflow
- Production and productivity impact on output or business continuity
- Safety, quality, and environmental implications
- Security and system control especially in regulated environments
- Reputation and stakeholder confidence
Once critical loads are identified, prioritize them by importance and required runtime.
For example:
- On-premise servers may only need enough power for a safe shutdown
- Medical or telecom equipment may require extended runtime or continuous power
This prioritization process is known as load shedding.
Need Help with Load Assessment?
If you're unsure how to classify your equipment, BT Connect offers detailed site surveys and energy assessments.
Our team of experts will help you:
- Identify critical and non-critical loads
- Recommend suitable UPS systems for each category
- Ensure continuity and reliability in your organizations operations
We are committed to delivering solutions that balance performance, safety, and cost-efficiency.
Critical Loads
These are devices or systems essential to the core operations of an organization and must remain operational during a power outage.
Examples include:
- Servers in data centers
- Life support equipment in hospitals
Any failureeven partialcan lead to severe consequences. For this reason, critical loads require uninterrupted power through a UPS or backup generators. In some cases, the objective is not continuous operation but enabling a safe shutdown to prevent data loss or equipment damage.
Non-Critical Loads
These are devices that can stop operating safely during a power outage because they are not essential to business continuity.
Examples include:
- Office printers
- Standard lighting
- Desk fans
Additional Load Categories for General Organizations
Essential Loads
- Not directly tied to business operations but important for safety and functionality
- Includes emergency lighting or critical ventilation
- These may not need continuous power but should run once the backup generator kicks in
Non-Essential Loads
- Acceptable to shut down during outages without impact on safety or operations
- Includes decorative lighting, coffee machines, or peripheral devices
Factors to Consider When Classifying Loads
Determining whether a load is critical or non-critical depends on:
- Financial impact potential revenue loss or customer service disruption
- Operational importance affects core functions or workflow
- Production and productivity impact on output or business continuity
- Safety, quality, and environmental implications
- Security and system control especially in regulated environments
- Reputation and stakeholder confidence
Once critical loads are identified, prioritize them by importance and required runtime.
For example:
- On-premise servers may only need enough power for a safe shutdown
- Medical or telecom equipment may require extended runtime or continuous power
This prioritization process is known as load shedding.
Need Help with Load Assessment?
If you're unsure how to classify your equipment, BT Connect offers detailed site surveys and energy assessments.
Our team of experts will help you:
- Identify critical and non-critical loads
- Recommend suitable UPS systems for each category
- Ensure continuity and reliability in your organizations operations
We are committed to delivering solutions that balance performance, safety, and cost-efficiency.
Related Content
Difference Between Line Interactive UPS and Online UPS
16 Jan 2025
How to Calculate UPS Load and Select the Right UPS Size
16 Jan 2025